

Instead, a so-called "bullet" coinage was used, consisting of bars of metal, thicker in the middle, bent round to form a complete circle on which identifying marks were stamped. Before 1860, Thailand did not produce coins using modern methods.
Coins Ĭowrie shells from the Mekong River had been used as currency for small amounts since the Sukhothai period.

#Us thai currency rates series#
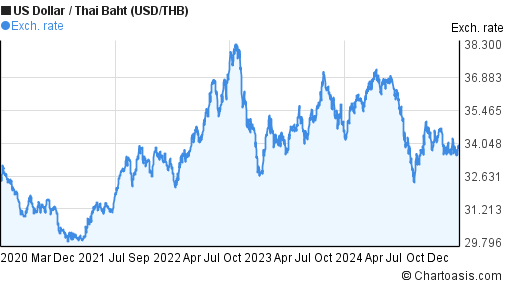
The baht was originally known to foreigners by the term tical, which was used in English language text on banknotes until the series 2 1925. It rose to 30 per dollar in January 2021. The baht was floated and halved in value, reaching its lowest rate of 56 to the dollar in January 1998. A strengthening US economy caused Thailand to re-peg its currency at 25 to the dollar from 1984 until 2 July 1997, when the country was affected by the 1997 Asian financial crisis. įrom 1956 until 1973, the baht was pegged to the US dollar at an exchange rate of 20.8 baht = one dollar and at 20 baht = 1 dollar until 1978. During World War II, the baht was fixed at a value of one Japanese yen on 22 April 1942. This was revised to 12 baht in 1919 and then, after a period of instability, to 11 baht in 1923. Beginning at 21.75 baht per pound sterling, the currency rose in value until, in 1908, a fixed peg to the British pound sterling was established of 13 baht per pound. In 1902, the government began to increase the value of the baht by following all increases in the value of silver against gold but not reducing it when the silver price fell. Before 1880 the exchange rate was fixed at 8 baht per pound sterling, falling to 10 to the pound during the 1880s. From 1856 to 1864, the values of certain foreign silver coins were fixed by law, with 5 baht = 3 Spanish dollar = 7 Indian rupees. This caused the value of the currency to vary relative to currencies on a gold standard. Until 27 November 1902, the baht was fixed on a purely silver basis, with 15 grams of silver to the baht. However, coins denominated in the old units were issued until 1910, and the amount of 25 satang is still commonly referred to as a salueng, as is the 25-satang coin. That system was in use up until 1897, when the decimal system devised by Prince Jayanta Mongkol, in which one baht = 100 satang, was introduced by his half-brother King Chulalongkorn along with the demonetization of silver bullet coins on 28 October 1904 after the end of silver bullet coin production by the opening of Sitthikarn Royal Mint in 1857. The smallest silver bullet coins available in the market. Solot here literally means "sixteen" or sixteenth, referring to the fractional amount relative to a fueang. These are listed in the following table: Unit ( RTGS)īia is Thai for cowry, the shell of which was used as a trade medium of the same value. These were pieces of solid silver cast to various weights corresponding to a traditional system of units related by simple fractions and multiples, one of which is the baht. Its currency value was originally expressed as that of silver of corresponding weight (now defined as 15 grams), and was in use probably as early as the Sukhothai period in the form of bullet coins known in Thai as phot duang. The Thai baht, like the pound, originated from a traditional unit of mass.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
